Biometric security is one of the most significant advances in the long journey to safe-guarding the digital world. Biometrics is an access control method that utilizes physical or behavioral features to authenticate the identity of a person and represents a powerful solution compared to the password.
With current development and innovativeness in technological devices, aspects of biometric authentication find themselves commonplace in as fundamental tasks as unlocking a smart phone to complicated financial product authorization.
Biometric Authentication: Definition and Overview:
This type of identification involves the use of other characteristics of human body such as fingerprints or facial recognition. Such traits can be fingerprints, facial structure, iris or retinal scans, voice identification and even other discriminating features such as typing cadence. This as opposed to passwords or Personal Identification Numbers that can be easily copied or compromised in one way or another; Biometric on the other hand cannot in any way be imitated.
Types of Biometric Authentication:
There are several types of biometric authentication methods, each with its own set of advantages and applications: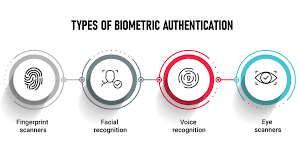
Fingerprint Scanning:
One of the most traditional ones, implemented used today in mostly in smartphones and access control system.
Facial Recognition:
Uses facial features in identification process, integrates into smart devices such as phones and security systems.
Iris Recognition:
Uses the rolling technique wherein photos capture the patterns of the iris due to the luxury it offers and its security.
Voice Recognition:
Describes different vocal parameters, utilized in customer care and militarily secure communication.
Behavioral Biometrics:
‘Keystroke logging’; keeps track of typing speed, or mouse speed, increases the level of protection.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Biometric Authentication:
Biometric authentication refers to the confirmation of an identity by comparing physical characteristics of an individual with their original documents.
Advantages:
High Security: The biometric traits are features inherent to human biology and hence cannot be easily forged.
Convenience: Convenience is one of the most important benefits as people do not have to remember numerous passwords in order to proceed to the next step of using a certain application.
Quick Verification: it accelerates the authentication process, particularly in environments that require stringent security.
Disadvantages:
Privacy Concerns: Biometric data unlike, for example, a password that can be reset as soon as one realizes it is with an unauthorized person, is permanent.
False Positives/Negatives: They may sometimes not read or recognize another individuals feature or rather identity in the right manner.
Cost: Biometric systems also have the disadvantage of location-specific costs, which result from the need for both the hardware and software components.
How Biometric Authentication Works?
Biometric authentication systems work on the fundamental concept of capturing a biometric measurement from the user (such as fingerprint scan), then formatting it into a digital signal, and finally checking against data stored in the system. The process generally involves the following steps:
Enrollment: First, there is the enrolment, which is the capturing and storing of the biometric data in the system.
Storage: Biometric data stored in a database or on the device must be protected against unauthorized access or modification.
Comparison: This results in proving that the presented biometric data matches the one stored in the database.
Decision: Thus the connection is made on restriction or permit comparison or deny and grant basis.
Enabling Biometric Authentication on Android Devices: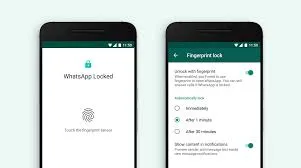
To enable biometric authentication on Android devices, follow these steps:
Access Settings: Open settings of the device you have on hand at the moment.
Security & Privacy: Access either ‘Security & Privacy’ or ‘Lock Screen & Security’.
Biometric Options: Decide which type of biometric authentication you wish to begin with (Fingerprint, Face Identification, etc. ).
Enroll Biometric Data: When prompted, enter your fingerprints, signatures, or other identity features to enroll yourself in the system.
Activate: To track user identification, turn on the biometric function for opening the device or making payments.
Biometric Authentication Devices and Software:
Devices:
Smartphones: Some devices even have fingerprints identification pads, face identification cameras, and even eyes identification scanners.
Access Control Systems: Incorporate biometric readers as security measures to strategic access points in spaces.
Laptops: The following are the features that should be implemented: Implement fingerprint scanners for log in functionality.
Software:
Voice Biometric Authentication Software: Frequently utilized in the call centres for safe and secure consumer authentication.
Biometric Authentication Apps: Examples of apps that adopt biometric data as a way of security.
Biometric Authentication Systems: BioSecurityNet works through a system of interconnected software modules designed to offer the complete solutions for implementing the biometric security in the different environments for the effective protection and authorization.
Behavioral Biometric Authentication:
Behavioral biometrics analyze patterns in user behavior, such as: Behavioral biometrics analyze patterns in user behavior, such as:
Typing Dynamics: It includes the speed of typing as well as the rhythm rate.
Mouse Movements: What one does with cursor.
Navigation Patterns: It is A user’s process of moving from one application to another in an optimal or unpredictive manner.
These methods provide extra security, to avoid situations where the biometric characteristics mapped on physical access are susceptible to violation, behavioral patterns would prevent such incidences.
Biometric Authentication in Banking:
The banking sector has been one of the most responsive industries deploying biometric authentication techniques to boost security as well as ensure easier services for consumers. Common applications include:
ATM Access: Withdrawing cash with fingerprints or scans from the eyes of the iris.
Mobile Banking: Login to the banking applications using facial ID or fingerprint instead of a serial number or access code.
Secure Transactions: Using voice recognition in order to confirm the completion of a transaction over the phone.
Multimodal Biometric Authentication:
Multimodal biometric authentication involves the use of more than one biometric for security and accuracy improvement. For instance, it has been known for a system to implement fingerprint and facial recognition to identify a particular user. The above approach helps to minimize the rate of false/positive/negative results and offers a better degree of confidence.
Integrating Biometric Authentication with Active Directory:
Biometric authentication can be discovered to work with Active Directory of an organization in order to reduce the user management problems together with making the systems secure. This integration allows:
Single Sign-On (SSO): This means that the biometrics login will act as the master login for the multiple applications that the users will be using.
Centralized Management: From the authorization server panel, administrators can easily control who is allowed access to web applications and their login details.
Enhanced Security: Linking up the Active Directory security strength with other methods such as the biometric authentication technique.
Biometric Authentication in Mobile Devices:
The emerging technology that has been highly active in the adoption of biometric authentication is the mobile devices. iOS and Android devices offer various biometric options, such as:

Face ID: One of them is the failed facial recognition technology by Apple Inc.
Touch ID: Apple’s biometric technology Specifically, some of the promising technologies that were prominent for future mobile convenient devices include the following: Apple’s fingerprint scanning.
Android Biometric Authentication: Biometric modalities it supports includes fingerprint, facial and iris. Herunterladen
Biometric Authentication Solutions and Tools:
The biometric authentication solutions and tools refer to the security mechanisms that use biological characteristics to verify the legitimacy of a person for entry into a given system.
Several companies provide comprehensive biometric authentication solutions:
Cisco: Provides powerful security solutions for business networks based on biometric parameters.
Microsoft Azure: Integrate biometric authentication and support cloud services.
Google Cloud: Allows for the inclusion of biometric authorization in applications through the use of APIs.
Biometric Authentication vs. Verification:
Authentication: Uses algorithms to validate user identity especially when taking a biometric measurement with the stored biometric data.
Verification: Is the process by which a system ensures that the user is really the one claiming to be before accessing or doing business with the system.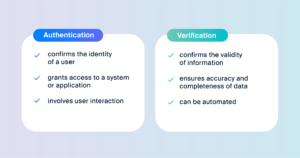
Future Trends in Biometric Authentication:
The future of biometric authentication looks promising, with advancements such as:
Enhanced AI Integration: Optimizing the performance of biometric systems for higher accuracy and faster response times.
Decentralized Biometric Authentication: Challenges of integrating biometric data into electronic devices include Storing biometric data locally to enhance privacy.
Multimodal Systems: On the basic of the introduction, it can be concluded that the utilization of at least two biometric techniques can be fruitful for enhancing the general security.
Biometric Authentication in the Medical Field:
When it comes to the healthcare industry, biometric authentication emerged as the most suitable choice when compared to other types of identity solutions.

Biometric authentication also has its application in healthcare whereby; authorized individual only gains access to patient data and the use of medical equipment. This minimizes the potential of leakage of information and guarantees that some information is accessed only by those with appropriate clearance levels.
Security and Privacy Concerns:
While biometric authentication offers numerous benefits, it also raises security and privacy concerns:
Data Breaches: From this point of view, biometric data is even more vulnerable than a password, which can be easily changed in case of a leakage.
Privacy Issues: Biometric data is sensitive information; therefore, its collection and storage have to reflect relevant policies.
Conclusion:
Biometric identification is a tool considered to be highly effective in the field of cybersecurity as well as being highly accurate and comfortable. They found out that technology will continue to feature in our lives strongly since it is plausible to believe that people are going to become more and more involved in technologies especially when it comes to financial instants and technology devices. It is only possible to really assess the feasibility of biometric authentication systems, both its advantages and drawbacks and the range of situations in which it can be correct to use them, based on their knowledge.
As advanced, the application of biometric authentications is expected to improve security while at the same time is convenient to use. This is especially in cases like securing a Smartphone, or protecting highly sensitive information or even in the security of financial transactions, biometric authentication remains one of the remarkable UAVS.





